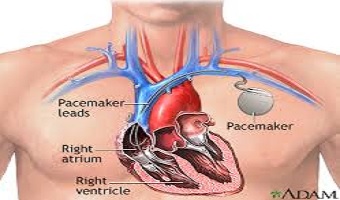
A pacemaker is a small device that's placed in the chest or abdomen to help control abnormal heart rhythms. This device uses electrical pulses to prompt the heart to beat at a normal rate. Pacemakers are used to treat arrhythmias (ah-RITH-me-ahs). Arrhythmias are problems with the rate or rhythm of the heartbeat.
Doctors recommend pacemakers for many reasons. The most common reasons are bradycardia and heart block. Bradycardia is a heartbeat that is slower than normal. Heart block is a disorder that occurs if an electrical signal is slowed or disrupted as it moves through the heart.
Heart block can happen as a result of aging, damage to the heart from a heart attack, or other conditions that disrupt the heart's electrical activity. Some nerve and muscle disorders also can cause heart block, including muscular dystrophy
.Types of Pacemaker
- Single chamber.
- Dual chamber
- Biventricular pacemakers
A pacemaker is implanted under the skin. ... A new "leadless" pacemaker is a self-contained unit that is implanted in the right ventricle of the heart. Using live x-rays to see the area, the doctor puts the leads through the cut, into a vein, and then into the heart. The leads are connected to the generator.
